No products in the basket.
Click and Collect – Please contact us to arrange collection or delivery of this item
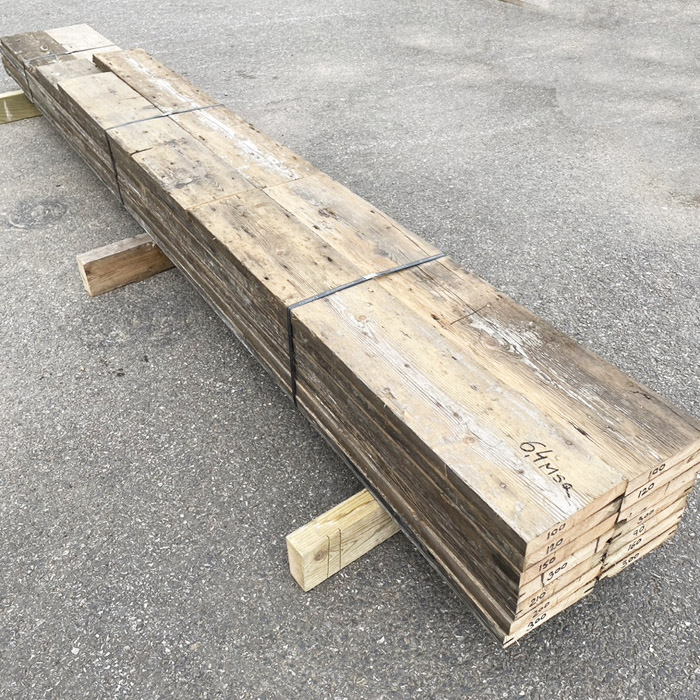
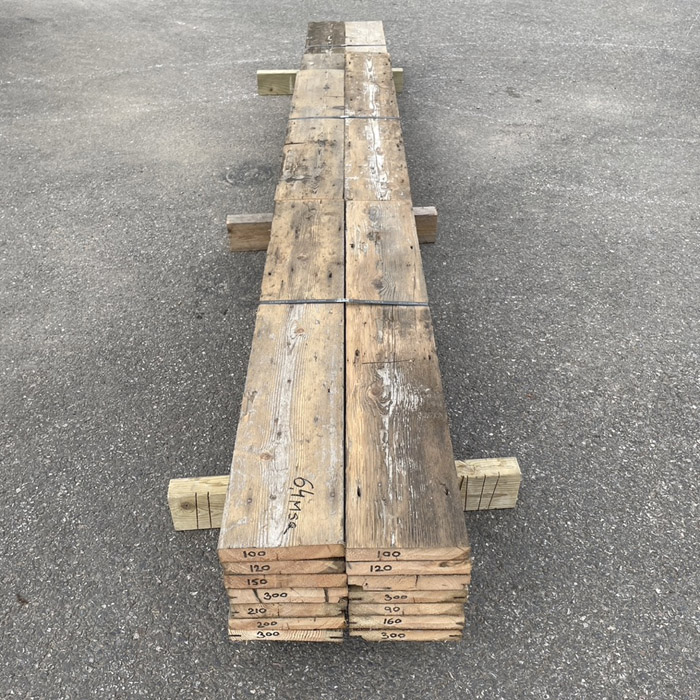
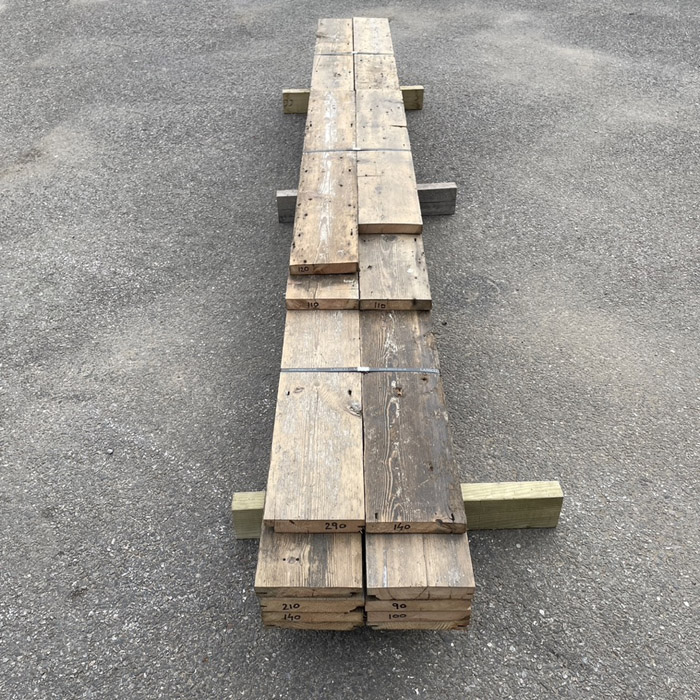
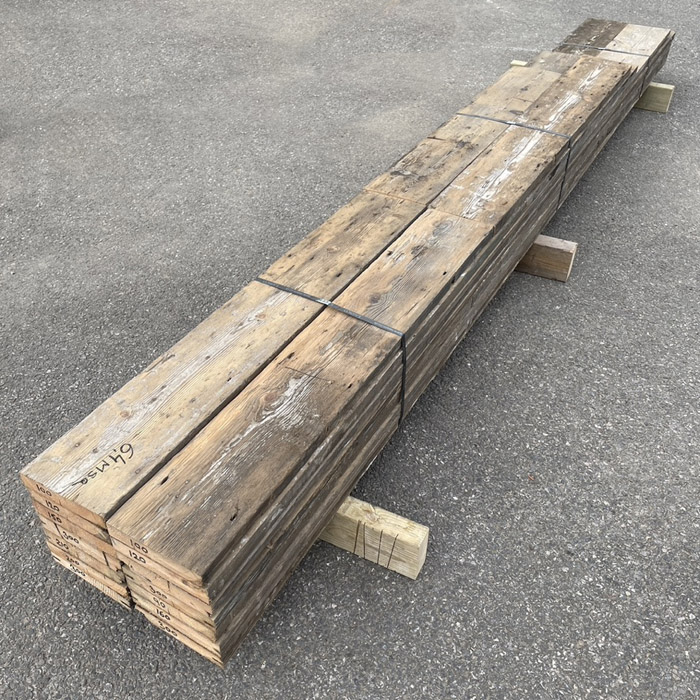
Reclaimed 6 1/2″ pine floorboards (6.5sqm ex Barnes)
salvaged from a yard in Barnes, BATCH SALE: 6.4square metres the parcel
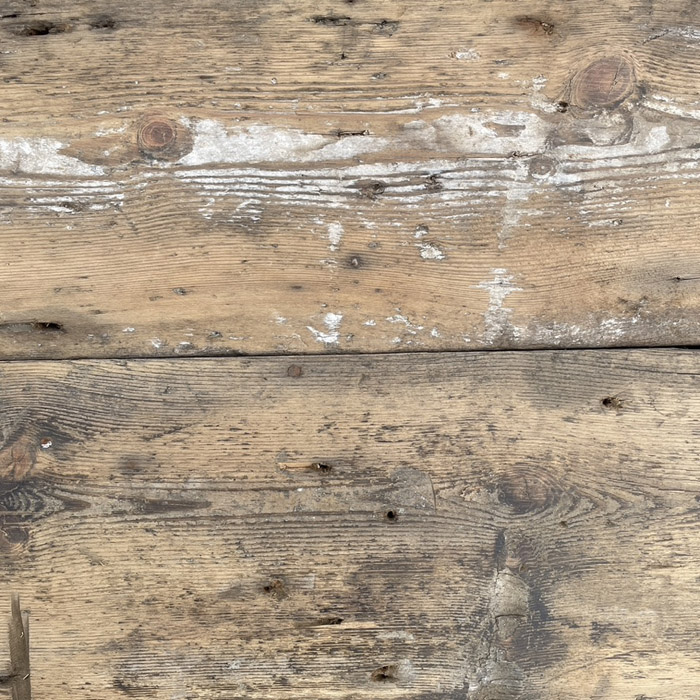
Square edge boards - formerly biscuit jointed - the edge could be re-laid with fresh biscuit joints . Distress and losses to the lower (thinner) flange of the edges - being thicker boards the upper flange has enough integrity to lay as per square-edged.
Condition: pewter patina, pleasantly worn with dints and scratches commensurate with age, surface nail holes but solid and uniform - good straight grain. 165mm wide; lengths across the batch: four at 3m, at least one other at 2m but the rest mostly shorts [35mm thick], (the shortness and thickness is reflected in the price). A useful bale of project timber.
£415 the batch (incl VAT)
Square-edged in a mixture of lengths, as salvaged. The old growth Baltic Pine from which these boards are made is straight grained and with a mellow pale yellow colour if sanded. These boards are supplied unfinished and they require cleaning, sanding and finishing for those not celebrating the old patina. Scroll through the pictures < > to see details of the timber.
Batch sale only.
The Building Conservation Society sums up the case for reclaimed pine flooring:
“The record demand for house building in 18th and 19th century London was an indicator of the nation’s prosperity. The demand for buildings resulted in a demand for timber; that timber was pine, felled in Poland and sent to England through the Baltic ports. The soaring popularity of imported softwood was driven by its quality and availability as well as favourable transport and conversion costs. The quality of slow-grown old-stand timber such as Pinus Sylvestris that was cut inland and sent down river to the Baltic ports of Memel and Riga was recognised by architects and craftsmen of the period. Contemporary specifications (for example by English architect Sir John Soane) called for pine and fir from these ports, including Memel and Riga Fir.
Much of our historic joinery and flooring was constructed from wood that was slow grown. This wood generally has a fine, close-grained texture and, because much of it was from old stands, it tends to be fairly clear of knots and vertically grained, giving it good durability and stability.
Today, managed softwood plantations aim to produce timber as quickly and as economically as possible. This faster grown timber is not as durable as that from the mature trees that were more common up to the start of the 20th century. Much of the modern fast-grown softwood will be used in construction once it has been pressure impregnated with preservatives. Generally this type of timber is not suited to quality repairs of historic joinery. The quality and closeness of grain of repair timber should match that of the original as closely as possible. This will reduce differential movement at the junction of old and new wood.”