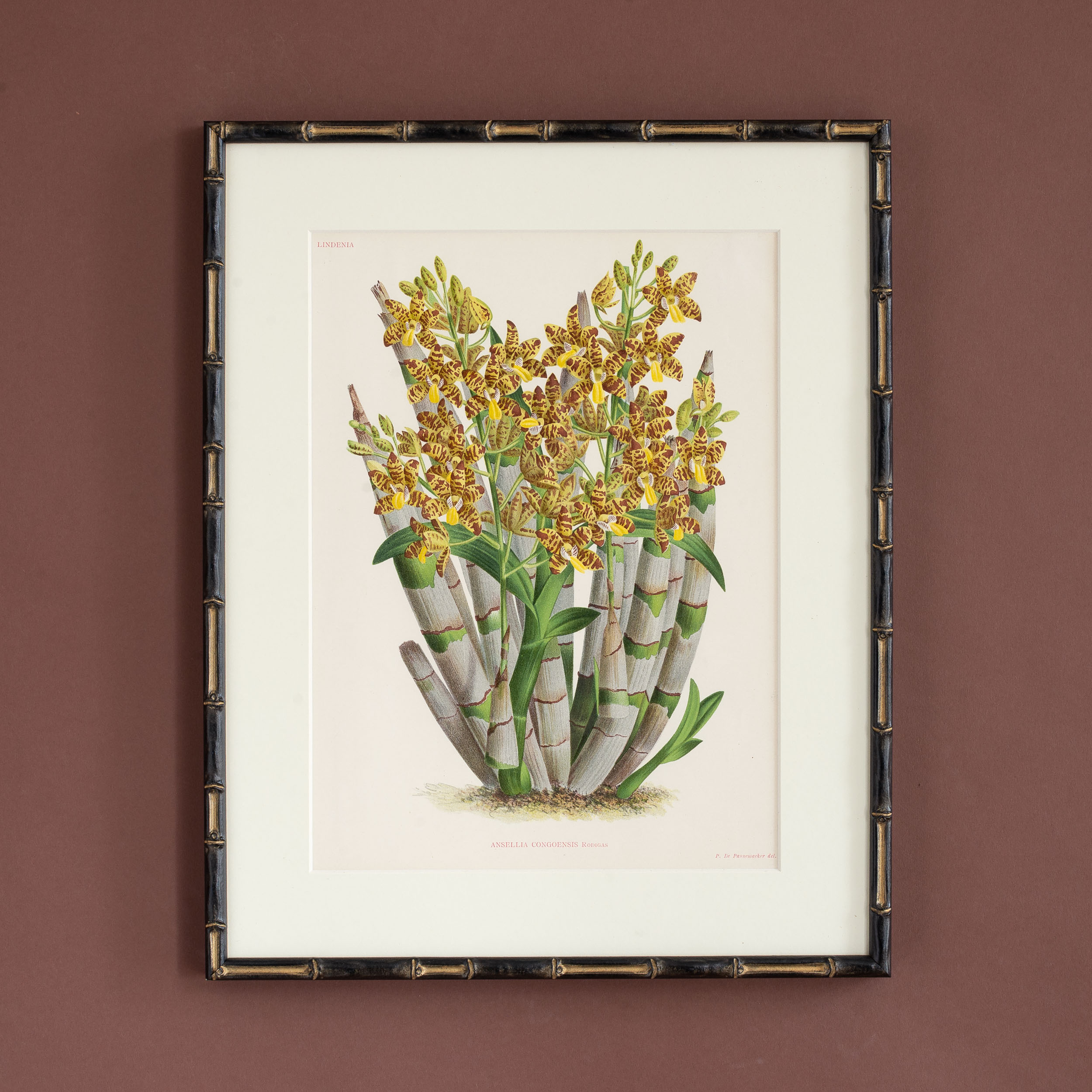
Linden Botanicals, Ansellia Congoensis,
L’Illustration Horticole, was a monthly horticultural review, founded in 1854 in Ghent, Belgium, by Ambroise Verschaffelt, a nurseryman who specialised in new plant introductions from South America. The lavish illustrations were produced by some of the very best botanical artists and lithographers – A. Goosens, P. De Pannemaeker and J. Goffart. The L’Illustration Horticole although founded by Jean Jules Linden (1817 – 1898) became a collaborative effort of many great horticulturists and field botanists of the day. Jean Linden in his own right was a renowned orchid grower and collector. Each monthly edition featured chromolithograph of botanical prints. Plants such as orchids, camellias, roses and leafy plants such as ferns and palm trees were represented. The magazine’s scope included pictures, descriptions, the history and culture of “the most remarkable plants,” new introductions, horticultural history, botanical expeditions, and accounts of the major expositions and of new works on botany and horticulture as well as garden descriptions and layouts.
£175 each
SOLD OUT
Out of stock
Published in Ghent c1875 for Linden’s L’Illustration Horticole. Mounted in cream and framed in faux bamboo.