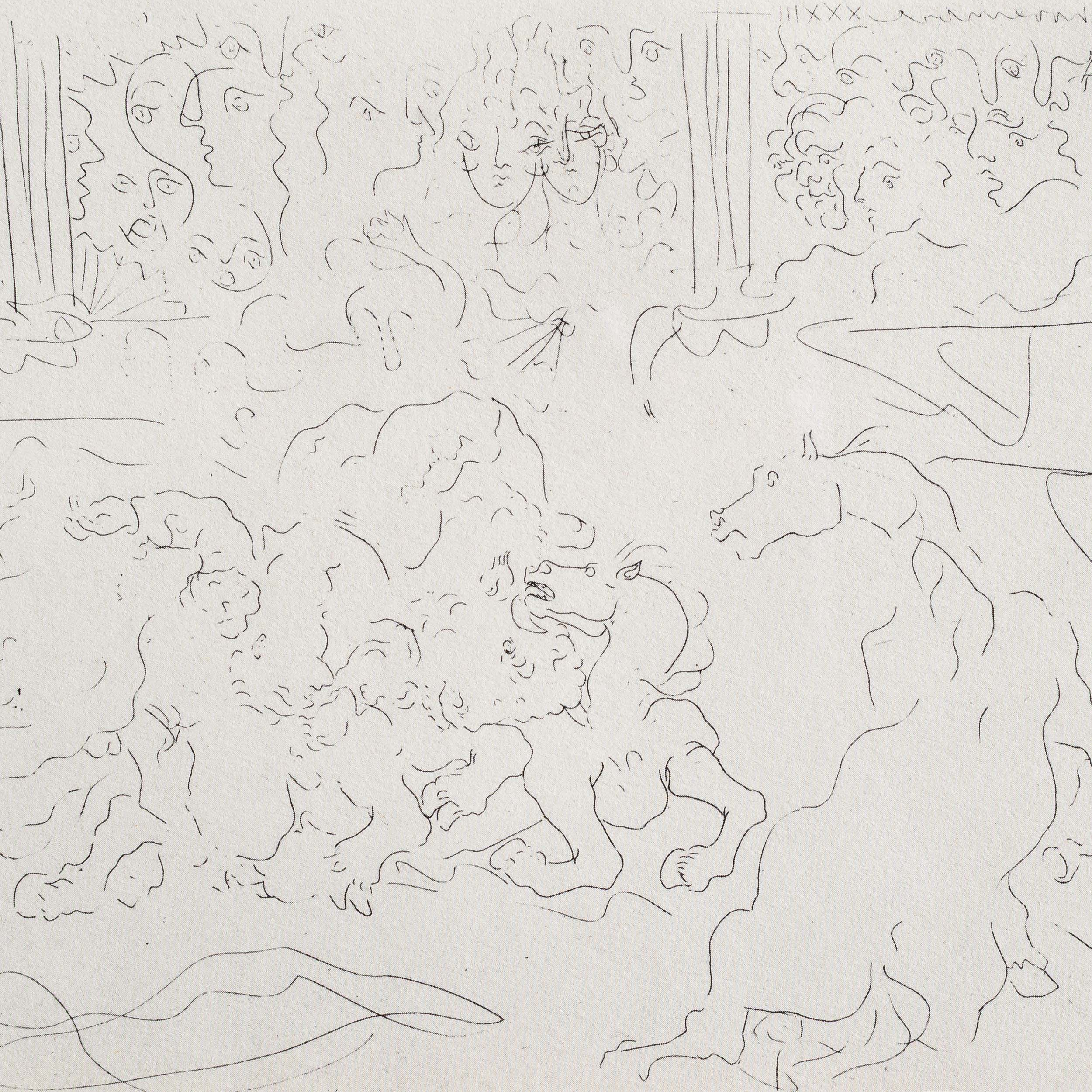
Picasso, Vollard Suite, 1956. Paris, November 7, 1933.
Original lithographs based on the earlier etchings.
Lithographs, published 1956 based on Picasso's work, produced from 1930-1937 for the art dealer Ambroise Vollard. Framed in plain oak with cream mounts.
Paris, November 7, 1933. Bullfight I
£175 each
In stock
In 1930 Pablo Picasso was commissioned to produce a series of etchings by the art dealer and publisher Ambroise Vollard in exchange for paintings by Pierre-Auguste Renoir and Paul Cézanne. The works were not based on a particular literary source or even individually titled, but reflected Picasso’s erotic and artistic obsessions in an era of political turmoil as fascism spread through Europe. Picasso worked extensively on the set in during the spring of 1933, and completed the suite in 1937.