No products in the basket.
Archived Stock - This item is no longer available
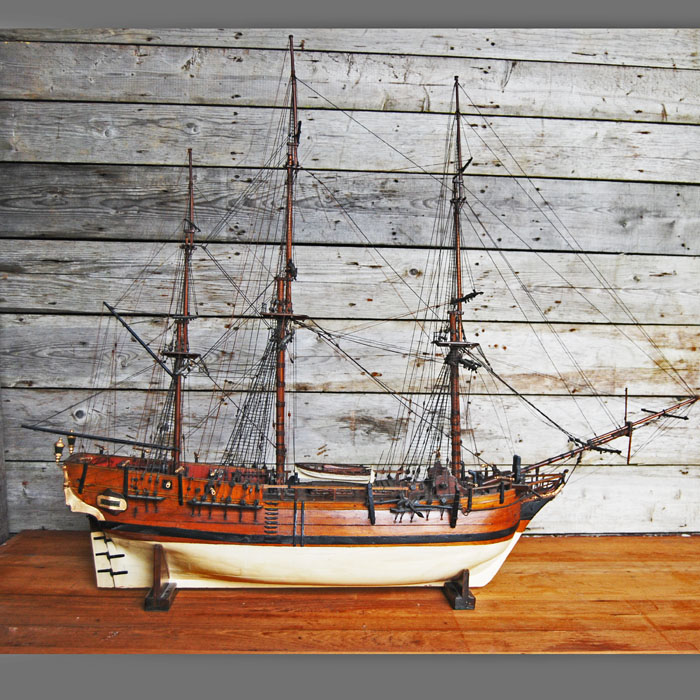
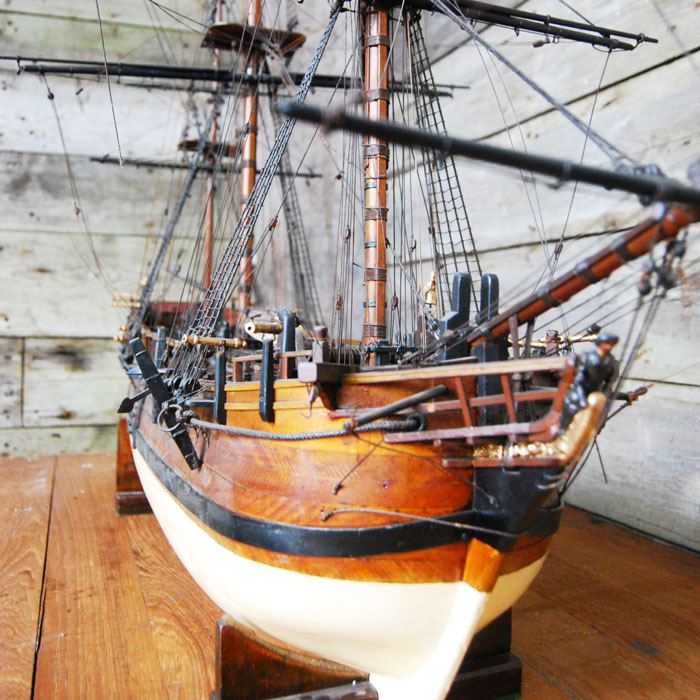
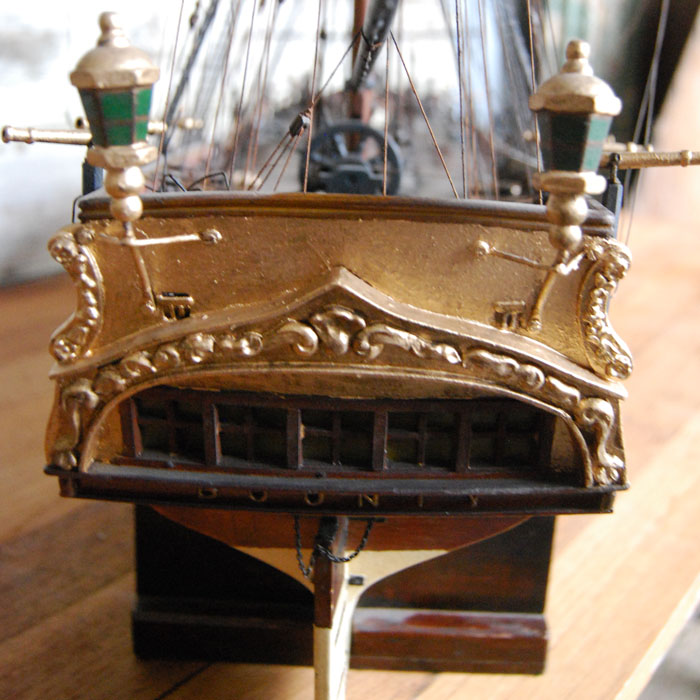
An English scratch-built timber model of HMS Bounty,
early 20th Century,
the fully rigged parcel gilded and painted frigate, detailed with life-boat, swivel guns and cannon, mounted on stands,
SOLD OUT
In stock
Bounty was originally known as collier Bethia, built in 1784 at the Blaydes shipyard in Kingston upon Hull, East Yorkshire, England. The vessel was purchased by the Royal Navy for £1,950 on 23 May 1787, refit, and renamed Bounty. The ship was relatively small at 215 tons, but had three masts and was full-rigged. After conversion for the breadfruit expedition, she was equipped with four 4-pounder (1.8 kg) cannons and ten swivel guns.
The ship had been purchased by the Royal Navy for a single mission in support of an experiment: The acquisition of breadfruit plants from Tahiti, and the transportation of those plants to the West Indies in the hope that they would grow well there and become a cheap source of food for slaves. The experiment was proposed by Sir Joseph Banks, who recommended William Bligh as commander, who in a turn was promoted through a prize offered by the Royal Society of Arts.
In June 1787, Bounty was refitted at Deptford. The great cabin was converted to house the potted breadfruit plants, and gratings fitted to the upper deck. William Bligh was appointed Commanding Lieutenant of Bounty on 16 August 1787, at the age of 33, after a career that included a tour as sailing master of James Cook's Resolution during Cook's third and final voyage (1776–80). The ship's complement was 46 men: a single commissioned officer (Bligh), 43 other Royal Navy personnel and two civilian botanists.
On 23 December 1787, Bounty sailed from Spithead for Tahiti. For a full month, the crew attempted to take the ship around Cape Horn, but adverse weather prevented this. Bligh then proceeded east, rounding the southern tip of Africa (Cape Agulhas) and crossing the width of the Indian Ocean. During the outward voyage, Bligh demoted Sailing Master John Fryer, replacing him with Fletcher Christian. This act seriously damaged the relationship between Bligh and Fryer, and Fryer would later claim Bligh's act was entirely personal.
Though Bligh is commonly portrayed as the epitome of abusive sailing captains, this portrayal has recently come into dispute. Caroline Alexander, in her 2003 book The Bounty, points out that Bligh was relatively lenient compared with other British naval officers.[6] Bligh enjoyed the patronage of Sir Joseph Banks, a wealthy botanist and influential figure in Britain at the time. That, and his experience sailing with Cook and familiarity with navigation in the area and local customs, were probably important factors in his appointment.[7]
Bounty reached Tahiti on 26 October 1788, after ten months at sea.
Bligh and his crew spent five months in Tahiti, then called "Otaheite", collecting and preparing 1015 breadfruit plants to be transported. Bligh allowed the crew to live ashore and care for the potted breadfruit plants, and they became socialized to the customs and culture of the Tahitians. Many of the seamen and some of the "young gentlemen" had themselves tattooed in native fashion. Master's Mate and Acting Lieutenant Fletcher Christian married Maimiti, a Tahitian woman. Other of Bounty 's warrant officers and seamen were also said to have formed "connections" with native women.
After five months in Tahiti, Bounty set sail with her breadfruit cargo on 4 April 1789. Some 1,300 miles (2,100 km) west of Tahiti, near Tonga, mutiny broke out on 28 April 1789. Despite strong words and threats heard on both sides, the ship was taken bloodlessly and apparently without struggle by any of the loyalists except Bligh himself. Of the 42 men on board aside from Bligh and Christian, 22 joined Christian in mutiny, two were passive, and 18 remained loyal to Bligh.
The mutineers ordered Bligh, two midshipmen, the surgeon's mate (Ledward), and the ship's clerk into the ship's boat. Several more men voluntarily joined Bligh rather than remain aboard. Bligh and his men sailed the open boat 30 nautical miles (56 km) to Tofua in search of supplies, but were forced to flee after attacks by hostile natives resulted in the death of one of the men. Bligh then undertook an arduous journey to the Dutch port of Koepang, located over 3,500 nautical miles (6,500 km) from Tofua. He safely landed there 47 days later, having lost no men during the voyage except the one killed on Tofua.
The mutineers sailed for the island of Tubuai, where they tried to settle. After three months of bloody conflict with the natives, however, they returned to Tahiti. Sixteen of the mutineers - including the four loyalists who had been unable to accompany Bligh - remained there, taking their chances that the Royal Navy would find them and bring them to justice. HMS Pandora was sent out by the Admiralty in November 1790 in pursuit of the Bounty, to capture the mutineers and bring them back to England to face a court martial. She arrived in March 1791 and captured fourteen men within two weeks; they were locked away in a makeshift wooden prison on the Pandora's quarterdeck. The men called their cell "Pandora's box". They remained in their prison until 29 August 1791 when the Pandora was wrecked on the Great Barrier Reef with the loss of 35 lives; four of them (Stewart, Sumner, Skinner and Hildebrand) were mutineers.
Immediately after setting the sixteen men ashore in Tahiti in September 1789, Fletcher Christian, eight other crewmen, six Tahitian men, and 11 women, one with a baby, set sail in Bounty hoping to elude the Royal Navy. According to a journal kept by one of Christian's followers, the Tahitians were actually kidnapped when Christian set sail without warning them, the purpose of this being to acquire the women. The mutineers passed through the Fiji and Cook Islands, but feared that they would be found there. Continuing their quest for a safe haven, on 15 January 1790 they rediscovered Pitcairn Island, which had been misplaced on the Royal Navy's charts. After the decision was made to settle on Pitcairn, livestock and other provisions were removed from Bounty. To prevent the ship's detection, and anyone's possible escape, the ship was burned on 23 January 1790 in what is now called Bounty Bay.
Thirty-five years later in 1825, HMS Blossom, on a voyage of exploration under Captain Frederick William Beechey, arrived on Christmas Day off Pitcairn and spent 19 days there. Captain Beechey later recorded this in his 1831 published account of the voyage, as did one of his crew, John Bechervaise, in his 1839 Thirty-Six years of a Seafaring Life by an Old Quarter Master. Beechey wrote a detailed account of the mutiny as recounted to him by the last survivor, Adams. Bechervaise, who described the life of the islanders, says he found the remains of Bounty and took some pieces of wood from it which were turned into souvenirs such as snuff boxes.